The weight distribution across the axles of Commercial Motor Vehicles (CMVs) is a critical aspect of road safety and infrastructure preservation. Regulating the weight on each axle and the total vehicle weight helps prevent damage to road surfaces and bridges, and ensures the stability and safety of the vehicle while in operation. Here's an overview of the key considerations regarding CMV axle weights:
Axle Weight Limits
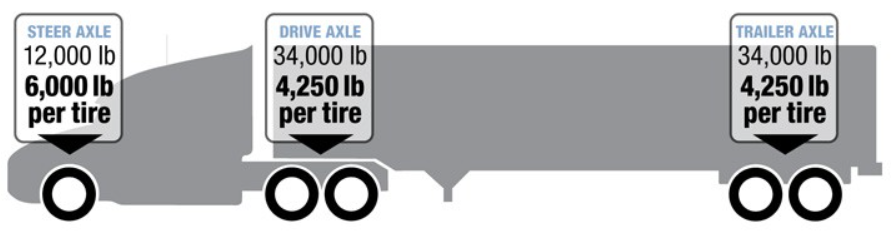
Federal Limits: In the United States, the Federal Bridge Gross Weight Formula, often referred to as the Bridge Formula, dictates the maximum allowable weight based on axle spacing and number. This formula aims to protect bridge structures from the stress of heavy loads. The maximum weight for a single axle is 20,000 pounds, and for a tandem axle group (two axles close together), it's 34,000 pounds under federal regulations.
State Variations: Individual states may impose their own weight limits for roads and bridges within their jurisdiction, which can sometimes be more restrictive than federal limits. It's crucial for CMV operators to be aware of and comply with the specific regulations in the states they operate.
Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR)
The GVWR is the maximum total weight of the vehicle, including cargo, fuel, and passengers, as specified by the manufacturer. The distribution of this weight across the vehicle's axles must comply with both federal and state regulations to prevent overloading.
Weight Distribution and Stability
Proper weight distribution is essential for the stability and safety of the CMV. Incorrect loading can lead to uneven weight distribution, affecting the vehicle's handling and increasing the risk of accidents, such as rollovers or loss of control.
Weigh Stations and Enforcement
CMVs are often required to stop at weigh stations along highways so that state officials can verify that the vehicle complies with weight regulations. Overweight vehicles can be fined and may be required to offload excess weight before being allowed to continue.
Impact on Infrastructure
Overweight and improperly distributed loads can cause significant damage to roadways and bridges, leading to costly repairs and maintenance. This is a primary reason for strict enforcement of axle and total vehicle weight regulations.
Special Permits for Oversize/Overweight Loads
For loads that exceed standard legal limits, special permits can be obtained. These permits may require specific routes to be followed, times of travel, and escort vehicles, depending on the size and weight of the load and the states through which the vehicle will travel.
Technologies for Monitoring
Some CMVs are equipped with onboard weighing systems that allow drivers to monitor axle weights in real-time, helping to ensure compliance with weight regulations and adjust load distribution as needed.
Importance of Compliance
Adhering to axle weight regulations is crucial for several reasons, including:
- Safety: Reducing the risk of accidents due to load shift or loss of vehicle control.
- Legal Compliance: Avoiding fines and penalties associated with violations.
- Infrastructure Preservation: Minimizing wear and tear on public roads and bridges.
- Operational Efficiency: Preventing delays due to regulatory non-compliance and ensuring the longevity of the vehicle.
In summary, managing the weight on each axle of a CMV is an essential part of compliance with transportation regulations, ensuring road safety, and preserving infrastructure. Proper planning, loading, and continuous monitoring are key practices for maintaining the appropriate axle and total vehicle weights.


.thumb.jpg.79710ba0be5a9f3be83fb45bcaf36e79.jpg)